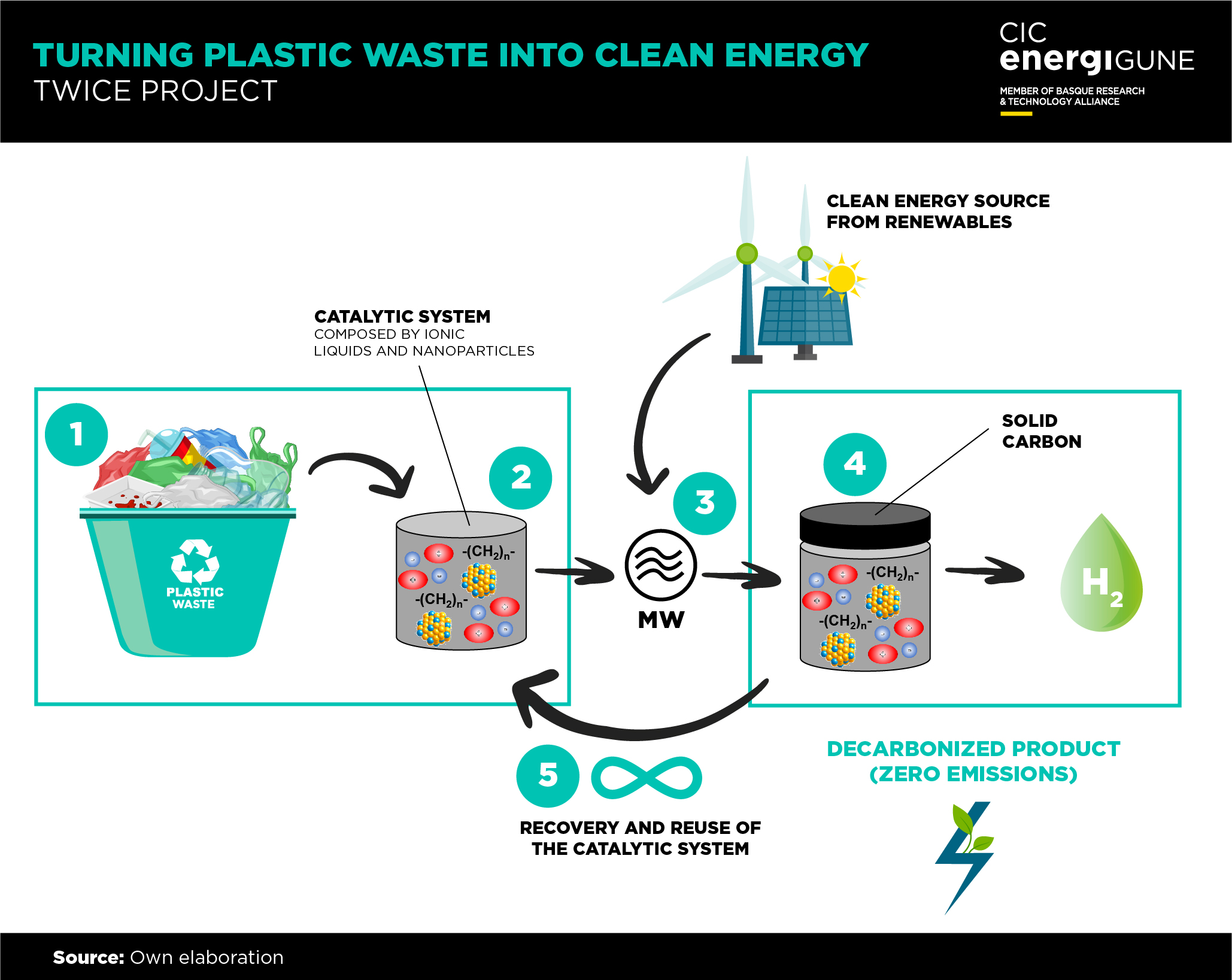
The proposal will contribute to the management of problematic plastic waste as well as the generation of decarbonized materials such as clean H2 and solid carbon combining two well-known technologies: catalysis (design, preparation, and characterization of innovative & recyclable IL-CATS) microwaves (more efficient use of the energy and less energy demanding process).
The Science Behind TWICE: A Deep Dive into Tertiary Recycling
TWICE proposes a novel method in which innovative Ionic Liquid-based catalytic systems (IL-CATS) are combined with microwave (MW) irradiation to selectively produce highly pure clean H2 and valuable decarbonized chemicals from plastic waste, thus addressing plastic waste remediation and sustainable energy generation closing the loop of circular economy and therefore responding to global climate change challenges.
Consequently, TWICE brings techno-economic and environmental outstanding advantages, which add to novelty significant breakthroughs compared to other routes stablished routes for tertiary plastic waste recycling and sustainable energy production:
- plastic waste catalytic deconstruction by single-step method at mild conditions (atmospheric pressure and temperature < 300 °C)
- fast production of pure H2 (> 97%) in high yield (> 97%)
- solid carbon co-product easy recoverable for its commercialization
- no catalyst coking and therefore long lifespan of the IL-CATS
- facile recovery and reuse of the IL-CATS
- significantly lower energy consumption due to MWs irradiation (efficient heating)
- high potential to offer clean H2 al low cost < 2 €/kg due to potential solid carbon sale revenues.
Ionic Liquids: The Game-Changing Component
Ionic Liquids (ILs) are the key of TWICE´s technology. These unique compounds, consisting entirely of ions which melts before decomposing and with negligible vapor pressure offer numerous advantages, including high thermal and chemical stability, recyclability, and the ability to be tailored for specific applications.
In TWICE, the unique features of ILs are taking to develop the ionic liquid-based catalytic systems where the ionic liquids play different roles such as to stabilize metal oxide nanoparticles (avoiding agglomeration), to enhance the solubility of olefinic plastic waste, to facilitate co-produced solid carbon recovery, to avoid active catalysts coking, to allow the recovery and reuse the entire catalytic system and in consequence to enhance the plastic catalytic deconstruction process making the whole process sustainable and economically feasible.
TWICE’s Scientific-Technical and Economic Impacts
On the one hand, TWICE is ambitious in terms of scientific-technical impact because it involves the efficient transformation of plastic waste into decarbonized products such as clean H2 and valuable carbon solid material covering three big challenges that scientific community must face the mitigation of the climate change, the production of sustainable energy and the management of huge amounts of problematic plastic waste. TWICE will unambiguously contribute to the decarbonization of the industrial sector and to reduce their dependence on foreign energy sources and feedstocks.
On the other hand, TWICE economic impact will be based in 4 main pillars:
- efficient innovative IL-CATS leading to increase selectivity to target decarbonized products, avoiding sintering and deactivation of catalytically active species, facilitating separation of the products avoiding costly downstream processes, lowering the overall temperature process saving energy and expensive downstream steps and consequently operating expenses (OPEX)
- the use of microwaves as heating source allowing to reduce the energy demand of the process compared to conventional heating
- the utilization of plastic waste as feedstock avoiding the cost associated to its management and further recycling procedures
- the valorization for further commercialization of the generated solid carbon material which selling will contribute to obtain incomes to reduce de final cost of the catalytic cracking process and the produced sustainable energy (H2).
Several key strategy sectors as potential beneficiaries of the revolutionary TWICE technology
In the long term, many sectors of activity will be able to benefit from the advantages of TWICE technology. The waste treatment sector will have a new route for the chemical valorization of plastic waste with extraordinary techno-economic efficiency and environmentally friendly. The chemical industry will have an inexpensive technology to produce sustainable energy (clean H2). Hydrogen storage and transport logistics could be simplified and made cheaper by storing/transporting the TWICE catalytic system instead of liquid or gaseous H2. This will also benefit hydrogen stations if they were equipped with a TWICE system for in-situ energy production. Finally, carbon nanomaterial users in different sectors (e.g., energy, automotive, sport) will take advantage of significant cost reduction in the production of carbon nanostructures that TWICE technology brings.