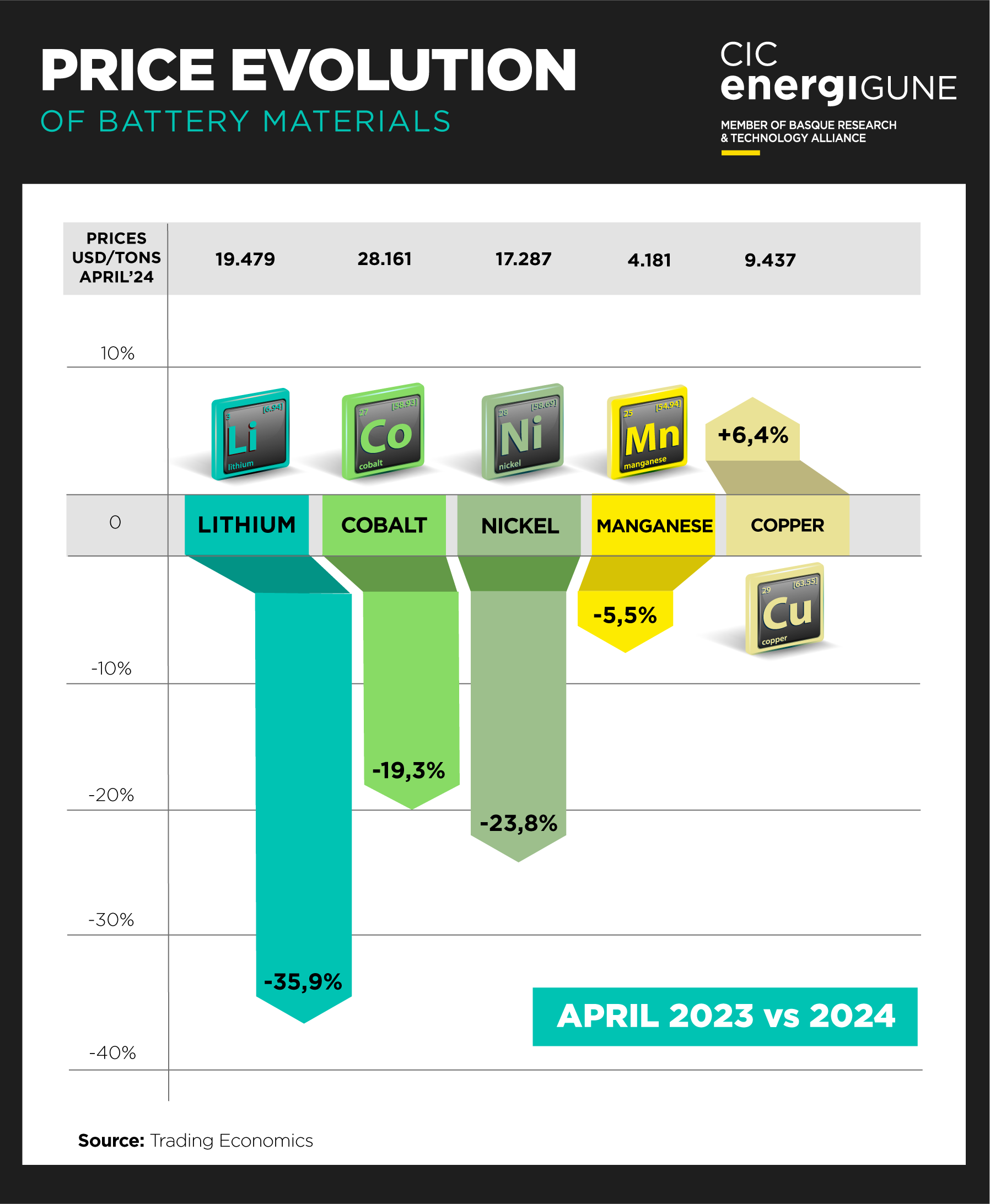
The market for key minerals for lithium-ion batteries, such as lithium, cobalt and nickel, has experienced a historic drop in prices. Lithium carbonate has traded at around $11,000 per tonne, down considerably from $70,000 a year earlier. With a decrease exceeding 80% for lithium from its highest peak between 2022 and 2023, the industry is forced to re-evaluate strategies and expectations.
In fact, the automotive industry is finding a path towards the manufacture of affordable electric vehicles. And that´s because according to BloombergNEF, the average price of battery packs fell to $139/kWh this year, down 14% from $161/kWh in 2022, marking the largest drop seen since 2018.
However, unlike previous years where innovation was the main driver of cost reductions, this year´s decrease is mostly attributed to lower raw material costs.
Redefining the Global Mining Landscape
It is the case of the global mining industry which is undergoing a significant transformation phase, influenced by this volatility in the prices of essential minerals for battery manufacturing. This transformation highlights the adaptability and varied responses of different regions:
- Australia, traditionally strong in the mining of these minerals, faces challenges with site closures and reductions in production, underscoring the need for adjustments in the face of falling prices.
- Latin America stands out for its resilience, thanks to lower extraction costs and strong lithium production, especially in countries such as Chile and Argentina, which use lower-cost salt deposits.
- Africa, with Congo as a leader in cobalt production, is working towards more sustainable and ethical mining practices, seeking to take advantage of global demand while facing logistical and regulatory challenges.
- Canada and Russia remain key players, with vast nickel and cobalt resources. These countries are looking to diversify markets and improve extraction technologies to maintain their competitiveness.
- China continues its dominance in rare minerals refining and lithium production, adapting quickly to market fluctuations and securing its position in the global supply chain through strategic investments.
This global picture reflects an evolving industry, with countries and regions adapting to new market realities through innovation, improved mining practices and expansion of production capacity.