The project is framed within the transformation of the electricity sector and the improvement of the efficiency of the use of energy. To this end, it is working on the generation of new materials that go beyond the state of the art of current electrochemical energy storage and thermal storage technologies applied specifically in two areas: alternative batteries to lithium-ion for stationary storage and thermal storage technologies applied to heat pumps.
Stationary electrochemical storage technologies beyond lithium-ion
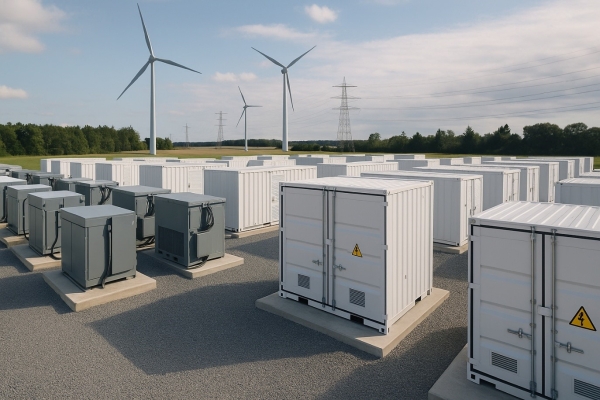
As we all know, battery energy storage is considered key to the development of the electric grids of the future. The use of batteries makes it possible to decouple the generation and consumption of electrical energy, being fundamental for grid integration with renewable energies, as well as to provide the grid with greater reliability, autonomy, stability and lower cost.
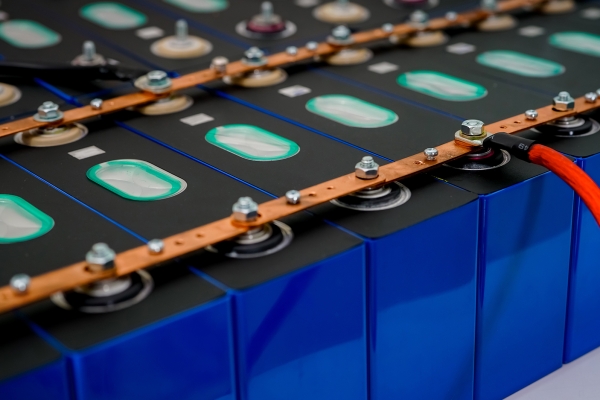
Lithium-ion batteries are undoubtedly the dominant technology in the market today due to the significant reduction in cost in recent years. However, this technology still has some technological and economic challenges to overcome to cover all the storage needs of the grid.
That is why, at CIC energiGUNE, we are researching alternative technologies to lithium-ion in order to meet the demand of the stationary sector.
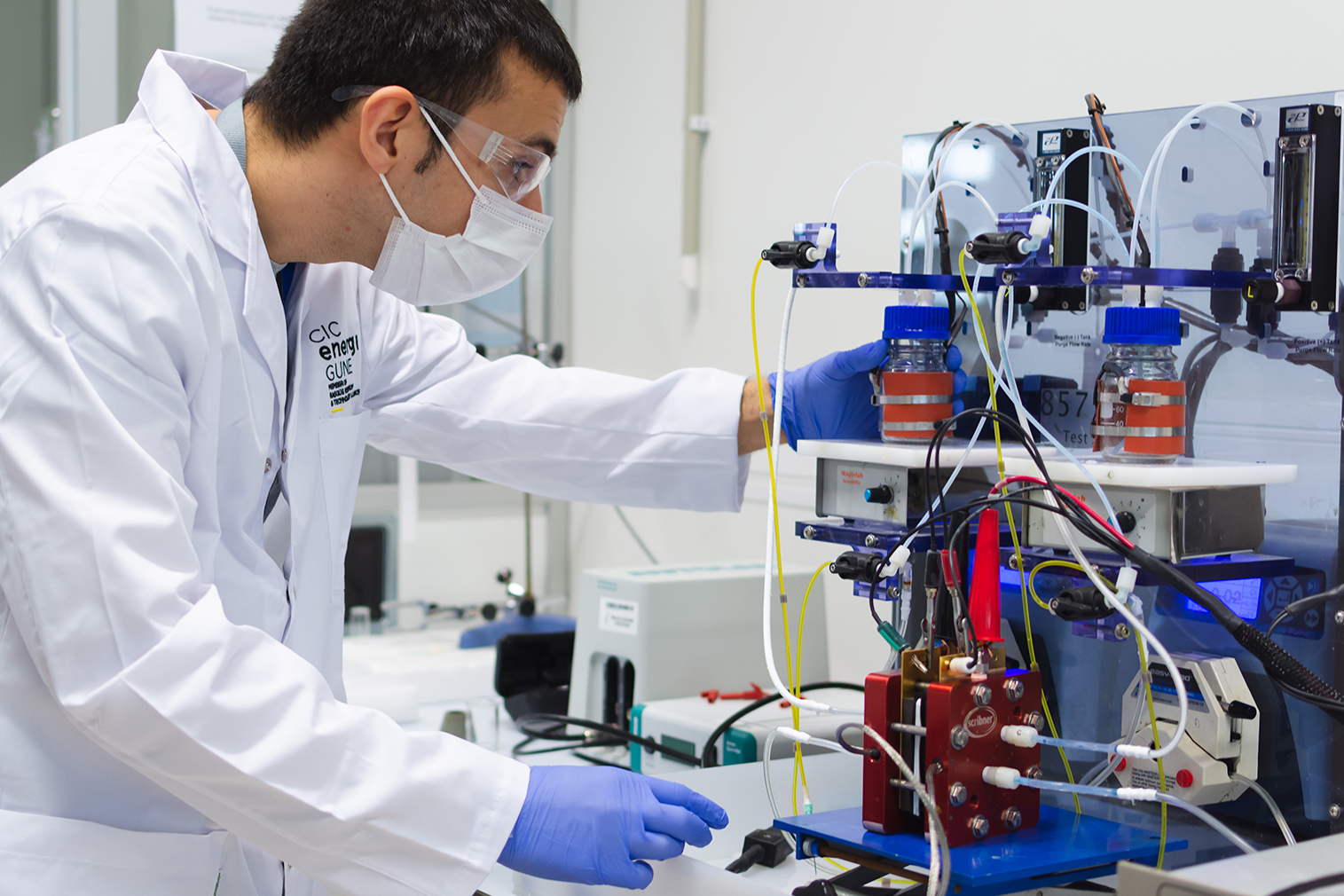
Specifically, the CICe2020 project is working on three lines of research applied to the stationary sector: materials and behavior of sodium batteries, development of materials for metal-air batteries and research on a new generation of redox-flow batteries based on an aqueous organic electrolyte.